The centre of origin is a geographical area where the particular group of organisms (either domesticated or wild) first originated on earth. Many people believed that centres of origin are also centres of diversity.
The concept of centre of origin is given Russian Scientist N.I. Vavilov 1926.
Centres of origin may be of two types
i) Primary centre of origin ii) Secondary centre of origin.
Primary centre of origin
The area where a crop has evolved from its wild species, showing maximum diversity is known as the primary centre of origin.
Secondary centre of origin
The area where certain crop species show considerable diversity of forms, although they did not originate there. Such centres are called secondary centres of origin.The main differences between centres of origin and centres of diversity are given below:
· Centres of origin are geographical areas where crop plants have originated.· A centre of diversity refers to a location where vast genetic variability for a crop and its wild species is found.
Importance of Centres of Origin
· The information on origin of crop plants is important in plant breeding to locate wild relatives, related species and new genes.· Knowledge of the origins of crop plants is important to avoid genetic erosion, the loss of germplasm due to the loss of ecotypes and habitat (such as rainforest) and increased urbanization.
· Germplasm preservation is accomplished through gene banks (largely seed collections but now frozen stem sections) and preservation of natural habitats (especially in centres of origin).
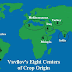
Initially, Vavilov proposed five centers of origin in 1924, which developed into eight in 1935, although his final papers (1992; 1997 posthumous publications) discussed seven major centers with minor additions. The eight centers of origins are as follows:
I. China center includes central and western China, Korea, Japan, and Taiwan. This is the native region for soybeans, millet, many vegetable crops, and fruits. Vavilov estimated that 20% of the world’s cultivated flora originates from eastern Asia. Eg. Sweet orange, Litchi, mandarin, persimmon, Japanese plum, Peach, Tea, Loquat, Kiwi-fruit, Mullberry Asian pear and apricot etc.
II. Hindustani center includes tropical India, Indochina, southern China, and the islands of southeastern Asia. This is the native land of rice, sugarcane, tropical fruit, and vegetables. More than 30% of the world’s cultivated plants originate here. Eg. Beal, Jack Fruit, Jamun, karonda, Kagji lime, Phalsa, chiraujii, Hog Plum, citon, Khirnii, Mahua, Kokkam, Lasoda, Pilu, sweet lime etc.
III. Inter-Asiatic center includes the interior mountains of Asia Minor, Iran, Syria, Palestine, Trans-Jordania, Afghanistan, inner Asia, and northwestern India. The native crops include the origin of wheat, rye, and fruit trees. An unbroken line from present day cultivated crops can be traced back to wild forms. About 15% of the important cultivated plants for the world originated here. Eg. Apple, almond, carrot, Pomegranate, walnut, carambola.IV. Caucasian center includes original species of temperate fruit trees. Additional species of wheat and rye, grapes fig, pear, quince, cherry, hawthorn etc.
V. Mediterranean center includes countries bordering on the Mediterranean Sea. Great ancient civilizations selected many vegetable and forage crops including olives and the carob tree. About 10% of the species of cultivated crops originated here. Eg. Olive, cole crops etc.
VI. Abyssinian center produced some important crops like niger seed oil plant (Guizotia abyssiniaca Cass.), a banana [Ensete ventricosum (Welw.) Cheesman], coffee (Coffea arabica L.) and castor bean. Probably about 4% of the world crops originated here.VII. Central American center includes southern North America, Mexico, and the west Indian Islands. Staple plants and subtropical fruits originated here. About 8% of the important crops of the world originated here. Eg. Sapota, Avacado, Papaya, Custard apple, Grape fruit, maize, cotton, beans, pumpkins, cocoa, avocados etc.
VIII. Andean center includes the Andean mountain range. This land produced many tuber-bearing crops such as potatoes, quinine tree, cocoa, passion flower, guava, heilborn, quinine tree, tobacco, cherimoya etc
Vavilov’s “centers” accounted for most of the major crops of global economic value of his day. He missed a few significant crops in North America, such as sunflower, and new crops, such as blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum) and strawberry (Fragaria ×ananassa), have globally developed since his time.Conclusions
N.I. Vavilov was a brilliant scientist who sacrificed his life for the science of genetics. His guidance for breeders to seek germplasm resistant to pest and diseases at his “centers of origin,” now more frequently called “centers of diversity,” has been proven to be directly applicable in many crop plants.References
Hummer, K. E., and Hancock, J. F. (2015). Vavilovian Centers of Plant Diversity: Implications and Impacts. HortScience horts 50, 6, 780-783
Bazilevskaya, N.I. & Bakhareva, S.N. 1991 N.I. Vavilov’s exploring expeditions and their importance Bull. Appl. Bot. Genet. Plant Breed. 140 12 23
https://nowgonggirlscollege.co.in
https://northgauhaticollegeonline.co.in